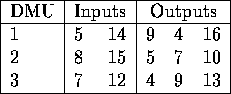
Consider analyzing the efficiencies of 3 DMUs where 2 inputs and 3 outputs are used. The data is as follows:

The linear programs for evaluating the 3 DMUs are given by:
min THETA st 5L1+8L2+7L3 - 5THETA < 0 14L1+15L2+12L3 - 14THETA < 0 9L1+5L2+4L3 > 9 4L1+7L2+9L3 > 4 16L1+10L2+13L3 > 16
min THETA st 5L1+8L2+7L3 - 8THETA < 0 14L1+15L2+12L3 - 15THETA < 0 9L1+5L2+4L3 > 5 4L1+7L2+9L3 > 7 16L1+10L2+13L3 > 10 end
min THETA st 5L1+8L2+7L3 - 7THETA < 0 14L1+15L2+12L3 - 12THETA < 0 9L1+5L2+4L3 > 4 4L1+7L2+9L3 > 9 16L1+10L2+13L3 > 13 end
The solution to each of these is as follows:
OBJECTIVE FUNCTION VALUE
1) 1.0000000
VARIABLE VALUE REDUCED COST
THETA 1.000000 0.000000
L1 1.000000 0.000000
L2 0.000000 0.411491
L3 0.000000 0.000000
ROW SLACK OR SURPLUS DUAL PRICES
2) 0.000000 0.000000
3) 0.000000 0.071429
4) 0.000000 0.000000
5) 0.000000 -0.007764
6) 0.000000 -0.060559 OBJECTIVE FUNCTION VALUE
1) 0.77333331
VARIABLE VALUE REDUCED COST
THETA 0.773333 0.000000
L1 0.261538 0.000000
L2 0.000000 0.226667
L3 0.661538 0.000000
ROW SLACK OR SURPLUS DUAL PRICES
2) 0.248205 0.000000
3) 0.000000 0.066667
4) 0.000000 -0.080000
5) 0.000000 -0.053333
6) 2.784615 0.000000
OBJECTIVE FUNCTION VALUE
1) 1.0000000
VARIABLE VALUE REDUCED COST
THETA 1.000000 0.000000
L1 0.000000 0.000000
L2 0.000000 0.480072
L3 1.000000 0.000000
ROW SLACK OR SURPLUS DUAL PRICES
2) 0.000000 0.000000
3) 0.000000 0.083333
4) 0.000000 0.000000
5) 0.000000 -0.009058
6) 0.000000 -0.070652
Note that DMUs 1 and 3 are overall efficient and DMU 2 is inefficient with an efficiency rating of 0.773333.
Hence the efficient levels of inputs and outputs for DMU 2 are given by:
![]()
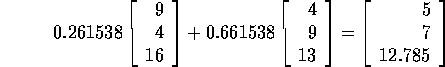
Note that the outputs are at least as much as the outputs currently produced by DMU 2 and inputs are at most as big as the 0.773333 times the inputs of DMU 2. This can be used in two different ways: The inefficient DMU should target to cut down inputs to equal at most the efficient levels. Alternatively, an equivalent statement can be made by finding a set of efficient levels of inputs and outputs by dividing the levels obtained by the efficiency of DMU 2. This focus can then be used to set targets primarily for outputs rather than reduction of inputs.