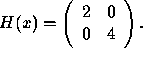Given a
function f of n variables ![]() ,
we define the partial derivative relative to variable
,
we define the partial derivative relative to variable ![]() , written
as
, written
as ![]() , to be the derivative of
f with respect to
, to be the derivative of
f with respect to ![]() treating all variables except
treating all variables except ![]() as
constant.
as
constant.
The answer is:
![]() .
.
Let x denote the vector ![]() .
With this notation,
.
With this notation, ![]() ,
,
![]() , etc.
The gradient of f at x, written
, etc.
The gradient of f at x, written ![]() , is the vector
, is the vector
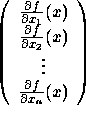 . The gradient vector
. The gradient vector
![]() gives the direction of steepest ascent of the function f
at point x.
The gradient acts like the derivative in that small changes around
a given point
gives the direction of steepest ascent of the function f
at point x.
The gradient acts like the derivative in that small changes around
a given point ![]() can be estimated using the gradient.
can be estimated using the gradient.
![]()
where ![]() denotes the vector
of changes.
denotes the vector
of changes.
![]()
In this case, ![]() and
and ![]() .
Since
.
Since ![]() and
and ![]() , we
get
, we
get
![]()
.
So 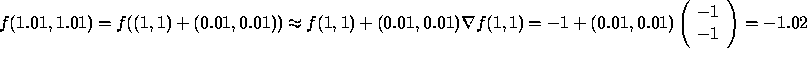 .
.

Hessian matrix
Second partials ![]() are obtained from f(x) by taking
the derivative relative to
are obtained from f(x) by taking
the derivative relative to ![]() (this yields the
first partial
(this yields the
first partial ![]() )
and then by taking the derivative of
)
and then by taking the derivative of ![]() relative to
relative to ![]() . So we can compute
. So we can compute
![]() ,
,
![]() and so on. These values are arranged into the Hessian matrix
and so on. These values are arranged into the Hessian matrix
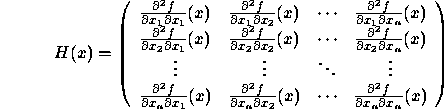
The Hessian matrix is a symmetric matrix, that is
![]() .
.
Example 1.1.1 (continued):
Find the Hessian matrix of
![]()
The answer is