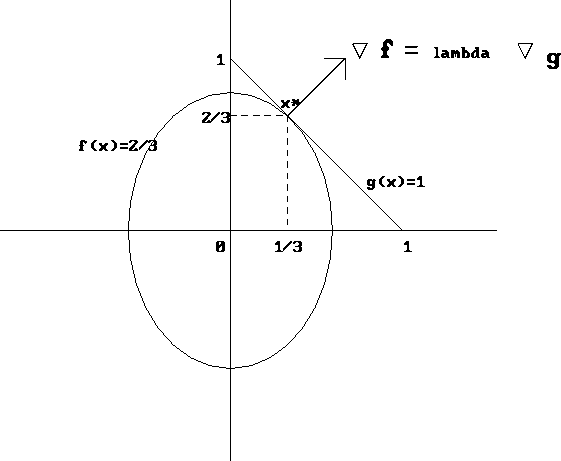
Figure 1.1: Geometric interpretation
There is a geometric interpretation of the conditions an optimal solution must satisfy. If we graph Example 1.1.2, we get a picture like that in Figure 1.1.

Figure 1.1: Geometric interpretation
Now, examine the gradients of f and g at the optimum point. They must point in the same direction, though they may have different lengths. This implies:
![]()
which, along with the
feasibility of ![]() , is exactly the condition
, is exactly the condition
![]() of Case (ii).
of Case (ii).